Hints from nature for ultimate chemical sensor
Thu, Sep 29, 2016-
Tags
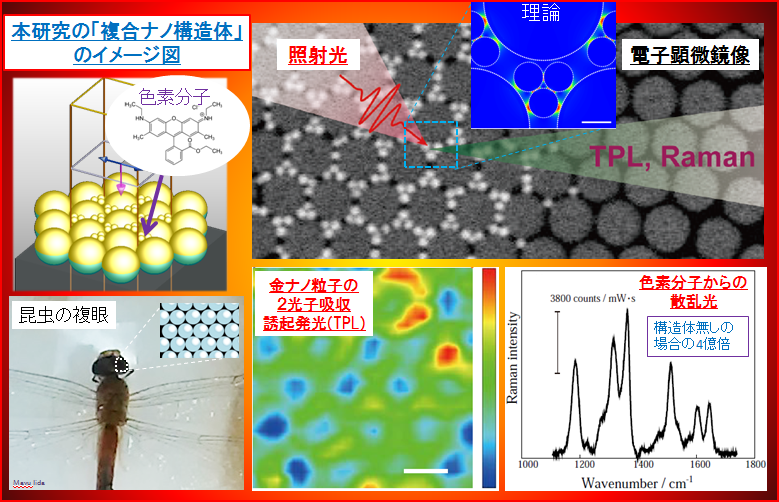
A research team consisting of Waseda University’s Professor Kohei Imura and Professor Takuya Iida of Osaka Prefecture University found a way to enhance optical response by coupling gold nanoparticle trimers with a gold film (gold-coated polystyrene microspheres) in two steps.
In daily life, silver and gold are silver and gold-colored, but if you take a look at these metals at a microscopic level, they change colors. Gold nanoparticles look red when electrons are moving rapidly. Because light gathers around electrons, light localizes near the gold nanoparticles. In such a case, if there are molecules, the molecules’ response to light become more sensitive. By understanding and using such a property, it is possible to create a chemical sensor which can determine molecule types and concentration. Moreover, if it can detect and distinguish the types of each, individual molecules, it will become the ultimate, highly sensitive chemical sensor. Hints on this research came from nature, for example, compound eyes of insects for having the highest photosensitivity in the wild and the phenomenon of lightning rods for effectively collecting light.
This research is promising for the effective use of localized light, which could enhance efficiency for solar energy conversion and be applied to a highly sensitive chemical sensors as mentioned above. Furthermore, the results could contribute to green innovation technologies for realizing a sustainable society as well as life innovation technologies for a healthy, long life through preventative medicine.
The team’s research was published in a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Chemical Society, the Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, on September 6.
The full article is available below.
Publication
Journal: Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters
Title: Multiple Resonances Induced by Plasmonic Coupling between gold Nanoparticle Trimers and Hexagonal Assembly of Gold-Coated Polystyrene Microspheres (Click on the title for the full article)
Authors: Takako Uchida and Kohei Imura from Waseda University; Takayasu Yoshikawa, Mamoru Tamura, and Takuya iida from Osaka Prefecture University