Research Theme
Study on spatial planning technology for “Medicine-Based Town” planning for a super‐aging and shrinking society
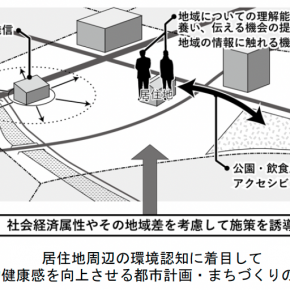
This study will specifically identify the ideal urban space and social systems from the perspectives of both medicine and urban planning, from the viewpoint of improving wellbeing, with regard to community development based on local medical care, welfare, and health, which are urgent issues for Japanese cities in the aging and shrinking society. We will also develop spatial planning techniques and evaluation methods for implementation.
Research Director
GOTO, Haruhiko
Faculty of Science and Engineering, School of Creative Science and Engineering
Project Members
- ARIGA, Takashi Professor, Faculty of Science and Engineering, School of Creative Science and Engineering
- GOTO, Haruhiko Professor, Faculty of Science and Engineering, School of Creative Science and Engineering
- LIN, Shuhsien Junior Researcher (Assistant Professor), Research Innovation Center
- MORIMOTO, Akinori Professor, Faculty of Science and Engineering, School of Creative Science and Engineering
- OKAMURA, Takeshi Senior Researcher (Assistant Professor), Research Innovation Center
- TANABE, Shinichi Professor, Faculty of Science and Engineering, School of Creative Science and Engineering
- HOSOI, Hiroshi
- MITANI, Kazuo
- NAKAMURA, Mika
- SATO, Hirosuke
- TAKAMINE, Shota
- TATSUMI, Yoshiko
- YOSHIDA, Michiro
- YOSHIE, Shun
Research Keywords
Wellbeing Spatial Planning
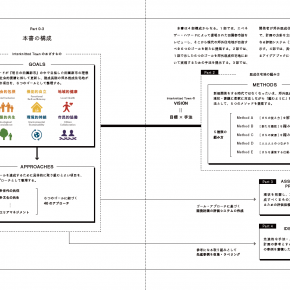
Research Summary
Based on the relationships with local governments, private businesses, and residents’ organizations that have been established thus far, the project will accumulate knowledge on social implementation
of private sector-led urban development through evaluation, planning, and demonstration of management activities in residential urban areas. (Major Objective 1)
In addition, focusing on wellbeing as a contemporary theme that straddles medicine, welfare, and health, we will establish new spatial planning techniques for renewal of residential urban areas with
the improvement of wellbeing as the evaluation axis. (Major Objective 2)
To this end, we will establish a planning system and practical theory to support medical care, welfare, and health throughout the region through the establishment of a wellbeing evaluation
method, the establishment of a scheme to improve wellbeing through residential area development and improvement of the working environment, and the construction of a framework for multi-agency
collaboration centered on private sector operators.
Specifically, the following six points will be set as objectives, which we aim to achieve within the research period.
(1) Establishment of evaluation methods for wellbeing in residential areas
(2) Establishment and theorization of an image of residential urban areas that support wellbeing in residential areas (including collaboration between medical and welfare institutions and residents’ organizations) and a scheme to realize this image
(3) Establish and theorize a scheme to realize wellbeing through the improvement of work-life balance.
(4) Establish and theorize a scheme to realize wellbeing through walkable urban development
(5) Establish and theorize a scheme to realize wellbeing through smart transportation
(6) Establishment and theorization of a method for building a framework for multi-agency collaboration, centered on private-sector businesses, for “Medicine-Based Town,” including the realization of wellbeing.