Scientists at Waseda University found a new method that provides a better approach for more efficient amide bond formation. Their study was published in Scientific Reports on February 13, 2018.
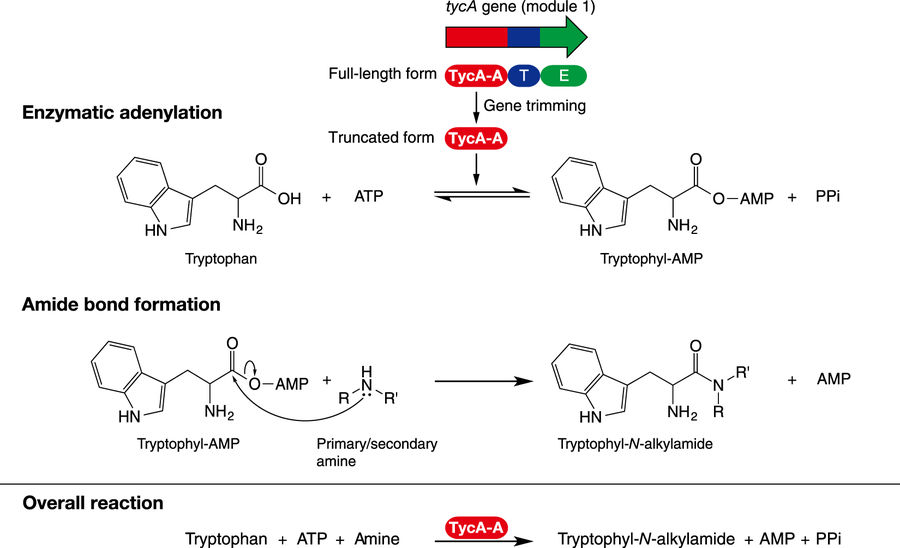
chemoenzymatic amide bond formation using the truncated adenylating enzyme, TycA-A
Amide bond formation is a fundamental reaction for synthesis of pharmaceuticals, bioactive peptides, food additives, flavors, nutrients, and polymers, as well as compounds for industrial applications. Though various methods for amide bond formation have been developed up to date, they suffer from low atom economy, meaning low conversion efficiency, and generate waste. Hence, a more efficient and environmentally-friendly amide bond formation was in demand.
To identify an alternative synthesis method, the scientists demonstrated L-tryptophyl-N-alkylamide synthesis by enzymatic adenylation of the carboxy group of L-tryptophan followed by nucleophilic substitution with diverse amines. Furthermore, the adenylation domain of tyrocidine snythetase 1 (TycA-A) showed a wide spectrum of substrate flexibility for both mono-substituted tryptophan and D-tryptophan.
Their findings are expected to facilitate the design for biocatalytic straightforward amide bond formation with less side products.
Reference
- A chemoenzymatic process for amide bond formation by an adenylating enzyme-mediated mechanism
- Published in Scientific Reports on February 13, 2018
- Authors: R. Hara, K. Hirai, S. Suzuki, K. Kino*
*Corresponding author: [email protected] - DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-21408-8








